Cobalt Market Faces Supply Surge Amidst Price Slump, IEA Report Reveals
Global – The International Energy Agency (IEA) released its “Global Critical Minerals Outlook 2024” on May 17, 2024, projecting a complex future for the cobalt market. The report indicates a significant increase in cobalt supply, driven by production growth in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Indonesia, coinciding with weaker demand, leading to subdued prices.
The IEA report highlights that while cobalt demand is rising due to the growing electric vehicle (EV) market, the trend toward low-cobalt or cobalt-free batteries is slowing long-term growth. In 2023, non-clean energy sectors, including portable electronics, accounted for 70% of total cobalt consumption, while EV batteries accounted for the remainder. However, the report notes that EV batteries will become the largest segment of cobalt demand by the end of this decade. Despite this, the growing market share of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which do not use cobalt, and the rise of alternatives like sodium-ion batteries are limiting cobalt demand.
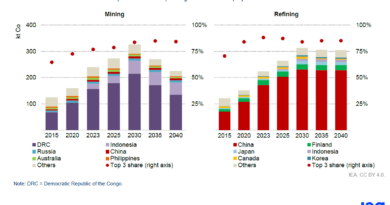
The report indicates that cobalt prices remained subdued throughout 2023 due to a combination of increased production from the DRC and Indonesia coinciding with weak demand. Over the past two years, mined cobalt supply expanded by an average of 16%, while refined cobalt supply increased by 13%. In 2023, prices for cobalt metal performed better than those for cobalt sulphate, signaling weaker demand in the battery sector compared with demand for alloys and magnets.
Key insights from the report include:
- Supply Growth: Mined cobalt supply expanded by an average of 16% and refined supply by 13% over the past two years.
- Price Decline: Cobalt prices remained low in 2023, with prices for cobalt sulphate especially affected.
- DRC and Indonesia: The DRC and Indonesia are the major suppliers of mined cobalt.
- Shift to Low-Cobalt: The trend toward low-cobalt or cobalt-free batteries is slowing the pace of long-term growth compared with other battery metals.
- Increased Nickel as a Source: Nickel plays a growing role as a primary mineral for cobalt production, especially with the rise of Indonesia’s nickel production.
- Artisanal Mining: Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) in the DRC has historically contributed significantly to cobalt supply, though its share decreased to 2% in 2023 due to lower prices.
The IEA report underscores that the geographical concentration of both mining and refining processes is intensifying. The DRC is poised for significant growth in mined cobalt production in the near future as several new mines ramp up their output. Indonesia has become the world’s second-largest cobalt supplier, with its production increasing twenty-fold in the last four years due to investments in domestic nickel-cobalt processing operations.
The report highlights that weak cobalt prices are threatening future production, with some projects facing delays and requiring additional funding. For example, the suspension of the Idaho Cobalt Operations project, the only primary cobalt mine in the United States, is attributed to low prices. Despite the current market conditions, some developers are still willing to invest in new projects. The report notes that stockpiling of cobalt may also have an impact on prices in the near future.
The IEA notes that while cobalt mining has traditionally been supported by hydropower in the DRC, the rise of energy-intensive operations in the DRC and the rise of Indonesia will increase the average emissions intensity associated with cobalt production. This indicates that strengthened regulatory and industry efforts are needed to reduce emissions from cobalt production operations.
The IEA’s analysis indicates that while the demand for cobalt is rising, the market faces an oversupply in the near term with an expected supply growth that outpaces demand growth. The report emphasizes that the future cobalt market will be shaped by the dynamics between the rising production in the DRC and Indonesia, the ongoing shift toward lower cobalt usage in batteries, and the ongoing environmental impact of mining and refining processes.
Historically, cobalt was primarily used in alloys and other industrial applications. However, the rise of EV batteries has transformed the cobalt market. The IEA report reveals that while EVs are driving demand for cobalt, the rise of LFP batteries may slow this growth. The report also indicates that the environmental and social costs associated with cobalt mining remain a major challenge that requires ongoing attention from industry and policy makers.